Let’s Start With Our Cosmic Backyard: How Big is the Solar System?
It took Voyager 1 a little over 36 years to leave the heliosphere, which is essentially the back yard of the solar system. But the region influenced by our sun’s gravity is much larger still.

Our Solar System & a Sense of Scale
Imagine that our entire Solar System were the size of a quarter. The Sun is now a microscopic speck of dust, as are its nine planets, whose orbits are represented by the flat disc of the coin.
So, how far away is the nearest star to our sun?
In our model, Proxima Centauri (and any planets that might be around it) would be another quarter, two soccer fields away. This is the typical separation of stars in our part of the galaxy.
Proxima Centauri is 4.243 light years away; which is 25 trillion miles from Earth. It would take 81,000 years to travel at conventional space craft speed (about 56,000 km/h) to our nearest interstellar neighbor.
To put this distance into perspective, here’s a time-scale perspective: at our top speed, it would take over 2,700 human generations to reach the nearest solar system.
By contrast, only 167 human generations have passed since the time of Dynastic Egypt.


The Formation of Earth
What about the Milky Way Galaxy?
The galaxy's central black hole, named Sagittarius A*, is much smaller and less massive than expected, based on the galaxy's overall size and mass.
The Milky Way has a "bar" structure, consisting of a dense concentration of stars running through its center, which was not predicted by earlier models of galaxy formation.
The Milky Way has a significant amount of dark matter, which is invisible and cannot be directly observed, but can be detected through its gravitational effects.
The Milky Way has a halo of millions of "dark" stars made of exotic material, such as low-mass brown dwarfs, or cold hydrogen-helium gas.
The galaxy's disk is much thicker than previously thought, with stars and gas clouds distributed in multiple layers.
The Milky Way galaxy has massive spirals arms which are much bigger than previously estimated.
We may be on the edge of a massive black hole that exist in the center of our galaxy.
There is evidence of a large number of exoplanets in the galaxy, and the possibility of many more yet to be discovered.
The Milky Way galaxy is moving toward a collision with the Andromeda galaxy, in about 4.5 billion years.
The galaxy is home to complex and varied life forms, and we are still discovering new forms of life on earth.

There are an estimated 500 billion stars in our galaxy.
The estimated number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy varies depending on the method used to make the estimation. But it is generally around almost 500 billion stars. Some recent research suggests that the Milky Way could have even more stars, up to a trillion stars or even more, which would put Milky Way among the biggest galaxy in our observable universe. However, this is still just an estimate and the true number of stars in the Milky Way may be different.
The sheer vastness of the galaxy makes it impossible to count every single star, so any variation in numbers are all based on estimates made using various techniques.
Yet, when you look up at the night sky, you think you see the universe … instead, all you see is the tiny rim of the circle (see below).
Milky Way Images
Did you know that every image you’ve ever seen of the Milky Way Galaxy is not real? The farthest we’ve ever sent a man-made object is just past the heliosphere of the solar system. We’ve never been far away enough to capture an image of our own galaxy. With our current technology, it would take billions of years to get far away enough to take a photo of our own galactic backyard.
Also, there could be 400 million planets in the Goldilocks Zone capable of supporting life in our galaxy alone.

HOW WE DETECT OBJECTS IN THE UNIVERSE
Because light from stars and their planets are so dim, astronomers and astrophysicists to use indirect methods to detect extrasolar planets. Several different methods have been created over the years - each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Most often, scientists use the subtle shift in light that occurs when a planet passes between its sun and our telescopes. We can also read the color spectrum of light that passes through its atmosphere to determine if that planet has water, vegetation, life and other chemical signatures.
HEAT SIGNATURES NEAR WATER SIGNAL POSSIBLE CIVILIZATION
Recently, astrophysicists detected an exoplanet with heat signatures along large bodies of water. While we cannot see the planet due to its distance, some scientists suspect that is a signature of intelligent life.
A SKEPTICAL VIEW OF THE ODDS

Ultra Deep Field
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field image has been shared so frequently it would seem an ordinary image of no significance. We talk about it as though its implications are common and widely understood; but few understand the infinitesimally small portion of the night sky it captured and what that single image says about the greater universe. If you found the darkest part of the night sky and stretched your arm in front of you with your thumb extended, the part of space captured by Hubble was no larger than an average thumbnail.
With that single image, scientists captured an estimated 10,000 galaxies.
In vibrant contrast to the rich harvest of classic spiral and elliptical galaxies, there is a zoo of oddball galaxies littering the field. Some look like toothpicks; others like links on a bracelet. A few appear to be interacting. These oddball galaxies chronicle a period when the universe was younger and more chaotic. Order and structure were just beginning to emerge.
The Ultra Deep Field observations, taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, represent a narrow, deep view of the cosmos. Peering into the Ultra Deep Field is like looking through a 2.5 metre-long soda straw.

Our Place in the Universe
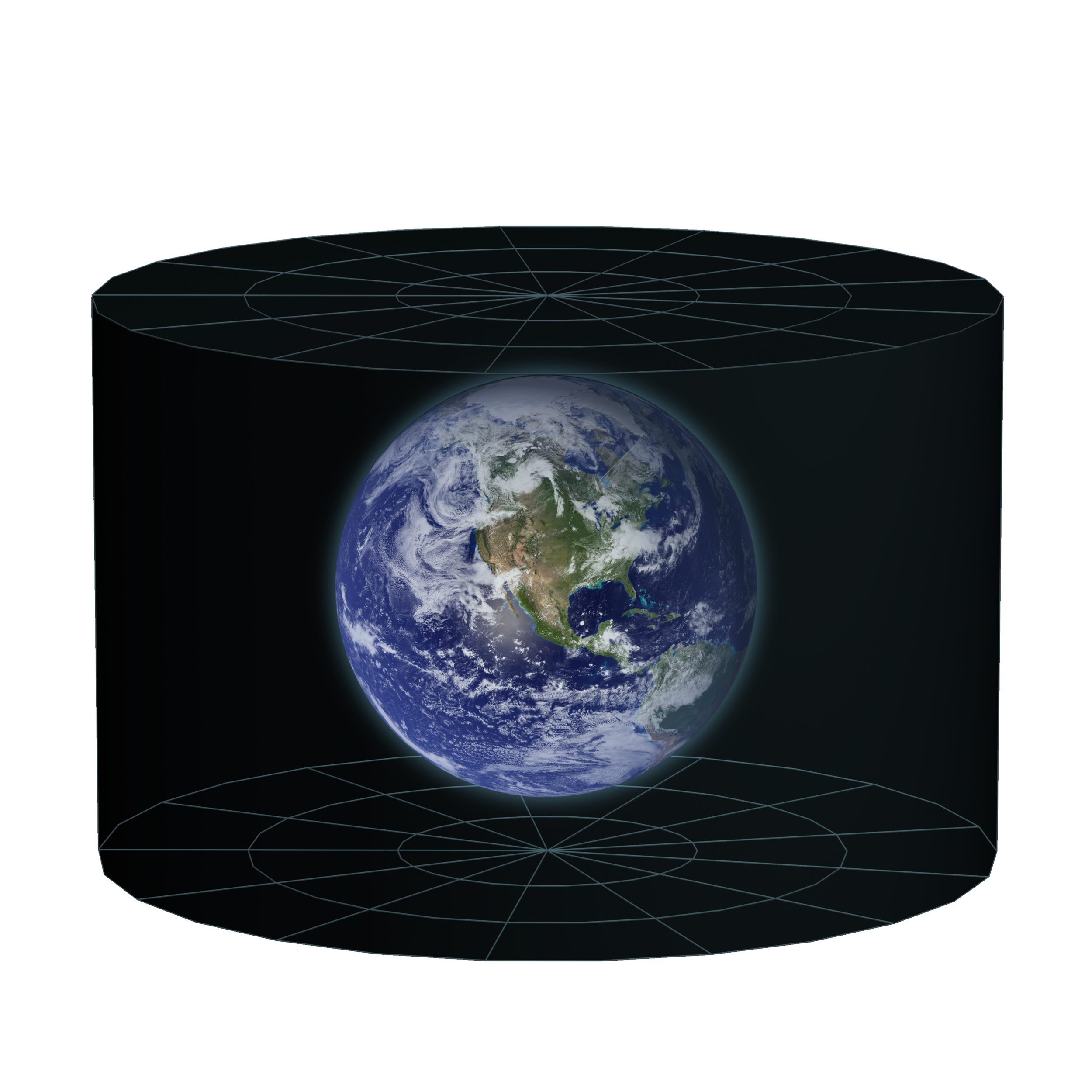
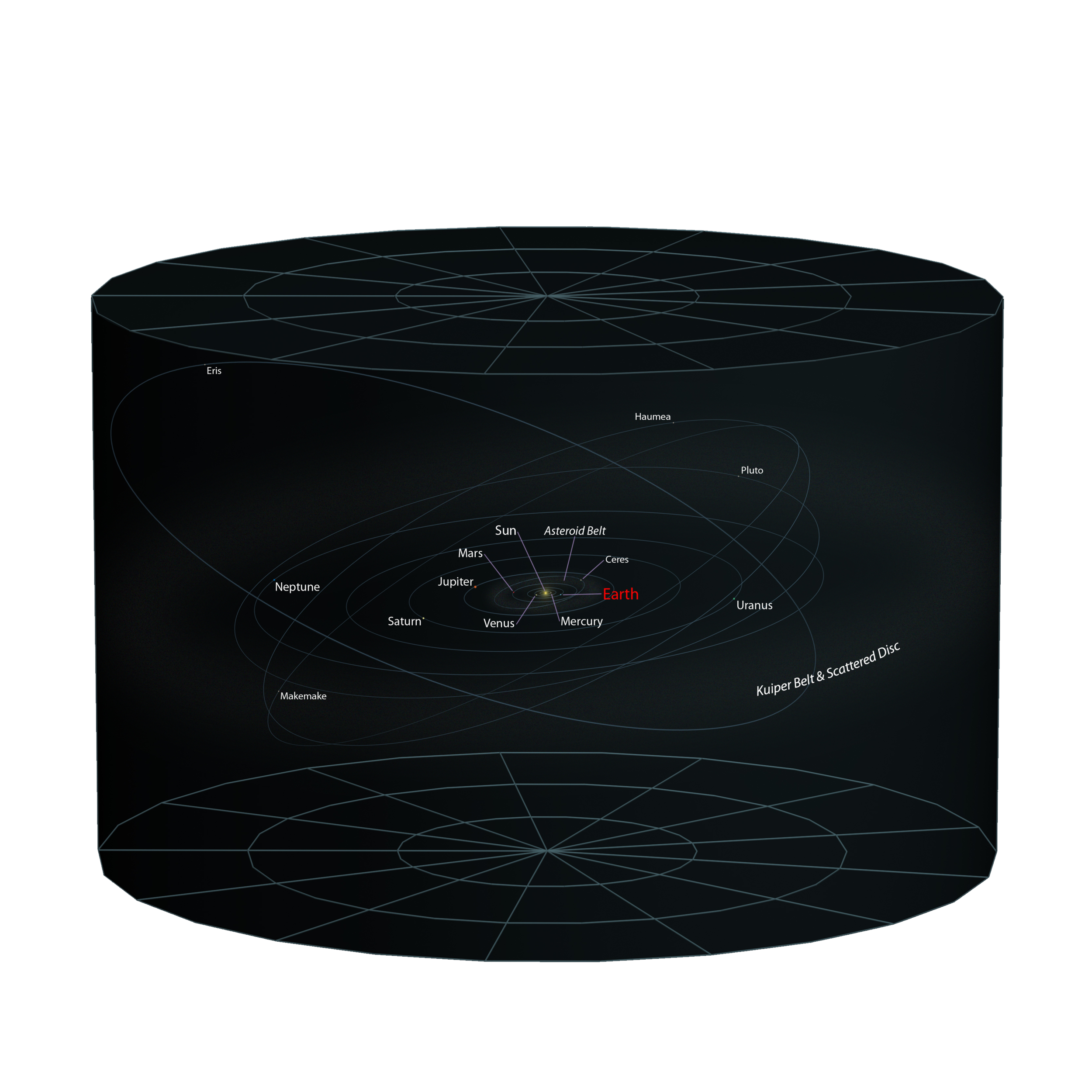



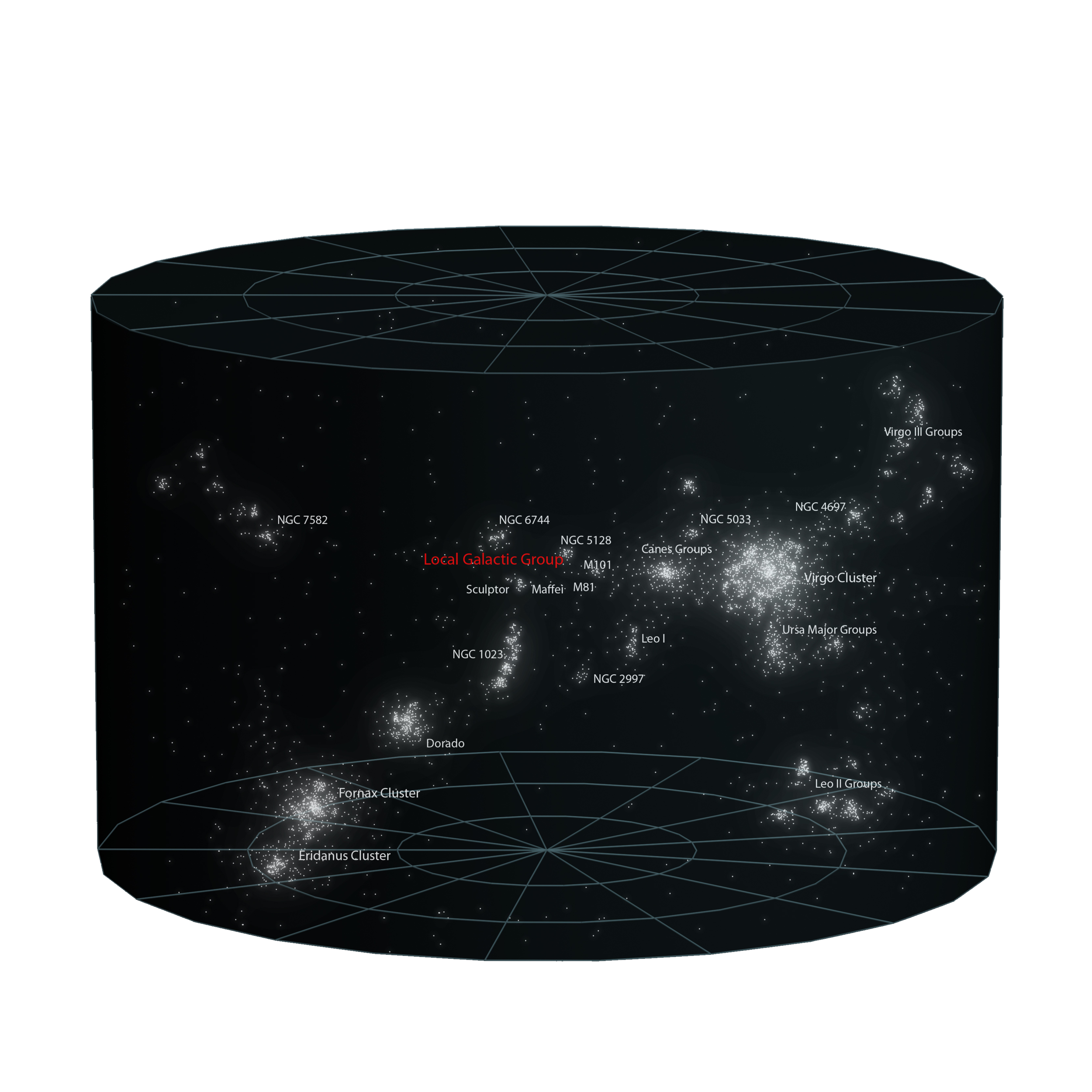
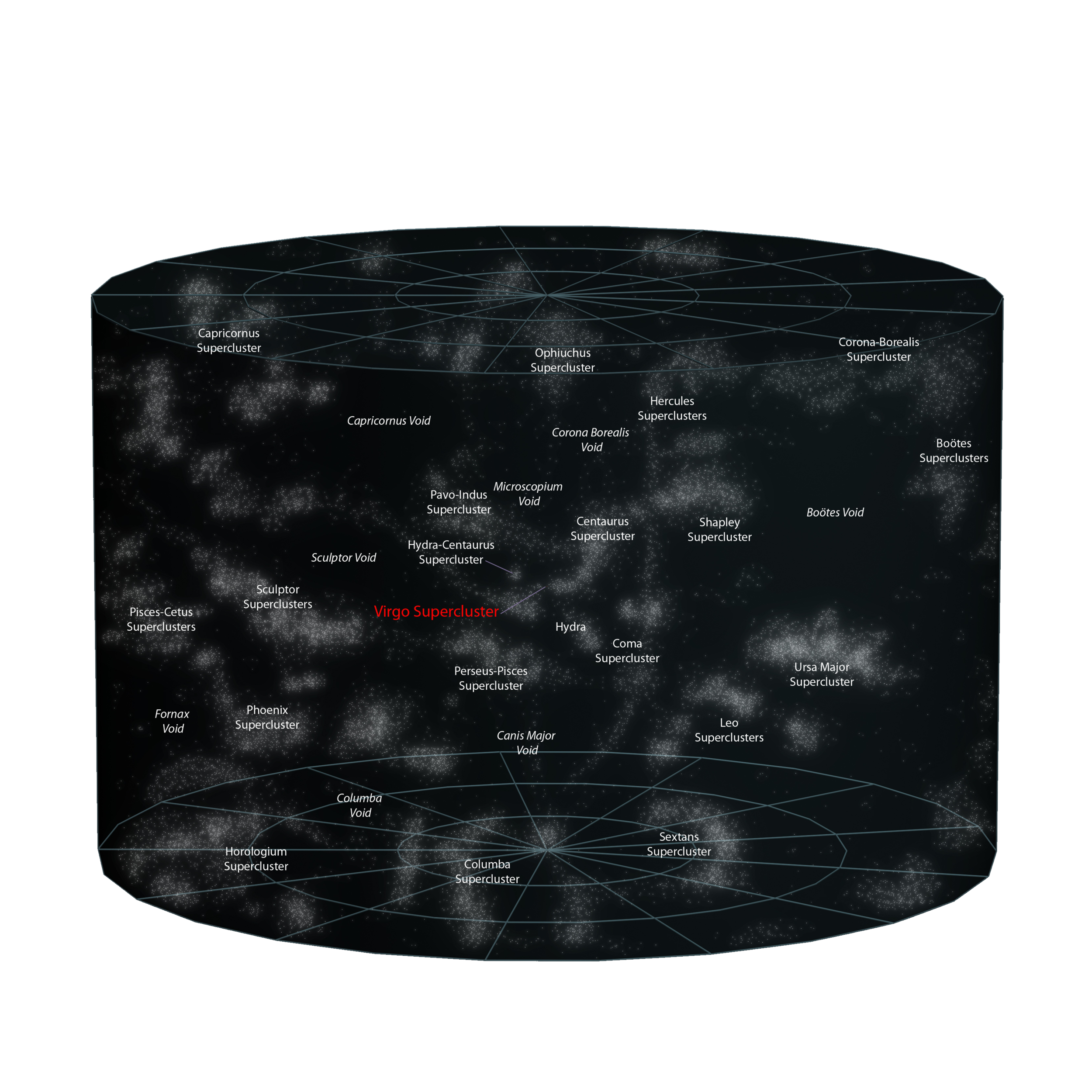

The Milky Way Galaxy has at least
There are at least 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe.

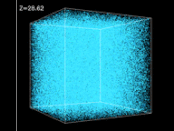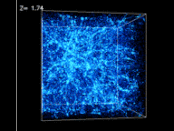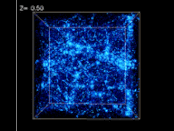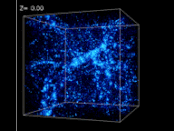
The voice of Carl Sagan with the most detailed three-dimensional map of the universe to-date.
To learn more about the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, visit here.

The Mysteries of Deep Space
Now that you have a sense of how infinitely enormous the universe is, let’s get weird. Because, the farther you go into the cosmos, the weirder things get. The laws of physics that govern existence on earth are turned on its head in the vast reaches of space.

Fascinating Facts
The Great Attractor
Have you ever had a nightmare where you're trapped and being dragged towards your inescapable doom? Well, you might not want to know, but on a galactic scale, we are living that nightmare right now. That's because, at a speed of 2.2 million kilometers per hour (human-fast, space-slow), the Milky Way, its companion galaxies, and various galactic hangers-on are all moving towards an area of space we don't know much about. The speed at which we are moving implies an area of space creating a massive gravitational force, roughly equivalent to 10,000 galaxies. And since it is sucking in everything within a considerable distance, this mysterious region has been dubbed "The Great Attractor." And if that isn't terrifying enough, we also can't see it.
The Great (and terrifying) Attractor sits in a region of space referred to by astronomers as the "Zone of Avoidance," which is ironic, because we can't avoid it. It's called that because it sits exactly on the other side of the densest part of the Milky Way, thus observing it through all those stars and massive clouds of space dust is nearly impossible. Nevertheless, astronomers have turned some of their instruments in the direction of the attractor, and determined that while there are a bunch of previously undiscovered galaxies in that region, there are still not enough to explain the force being exerted.
This leaves the true source of our eventual doom as either a previously inconceivable gravitational mass that we can't identify, or perhaps the interstellar equivalent of an internet dating serial killer: obscuring its identity behind a perfectly crafted profile to entice everyone within reach and draw them inexorably into their grubby space-van with blacked-out windows, dirty carpet, matching shovel accessories, and an entire superclusters' worth of chloroform..
The Largest Known Black Hole
TON 618 is the largest black hole detected to-date. It has a mass of 66 billion times our sun’s mass.
The Triangulum Galazy of about 40 billion stars has a mass of about 50 billion times our Sun’s mass.
TON 618 is heavier than an entire galaxy.
Supervoid
There is a place in space that 1.8 billion light-years across and is the largest structure ever discovered in the universe. Astrophysisics do not know what it is and why it is void of light or observable matter of any kind.
Web
Placeholder
Called the eXtreme Deep Field, or XDF, the photo was assembled by combining 10 years of NASA Hubble Space Telescope photographs taken of a patch of sky at the center of the original Hubble Ultra Deep Field. The XDF is a small fraction of the angular diameter of the full moon.
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small area of space in the constellation Fornax, created using Hubble Space Telescope data from 2003 and 2004. By collecting faint light over many hours of observation, it revealed thousands of galaxies, both nearby and very distant, making it the deepest image of the universe ever taken at that time.
The new full-color XDF image is even more sensitive, and contains about 5,500 galaxies even within its smaller field of view. The faintest galaxies are one ten-billionth the brightness of what the human eye can see.
THE BIG BANG
The Big Bang is often misunderstood; matter didn’t simply explode into being from nothing, the Big Bang happened everywhere in the universe simultaneously—it’s not an explosion in space but an explosion of space.